Why Choose a Fast Level 2 EV Charging Station for your Home
Today, there are three primary types of EV (Electric Vehicle) charging stations with a fourth under development. Charging equipment is classified by the speed, or rate, at which the vehicle batteries are charged. The rate of charge is a function both of the supply voltage and amperes. 
Types of EV Charging Stations 
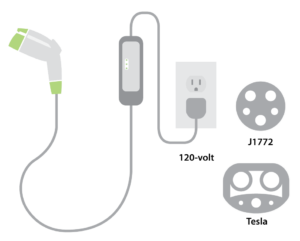
Nearly all new electric vehicles come standard with a Level 1 AC (Alternating Current) car charger, or slow charger. A level one cordset receives power from a standard 120-volt, 15 or 20 amp receptacle. The cordset comes with a vehicle connector, generally an SAE J1772 charge port on one end, and a NEMA (National Electrical Manufacturers Association) 120-volt standard receptacle plug on the other. These types of EV charging stations provide a power rate around 3kW, or 3,000 watts. The charge time for a level one charger generally ranges from 10 to 14 hours and is well suited for overnight charging at home.
As a second option offered by most electric vehicle manufacturers, and various third-party suppliers, is a Level 2 AC electric car charging station, or fast charger. The output connection is the same as a level one charger using the J1772 charge port that connects the charging unit to the electric vehicle. 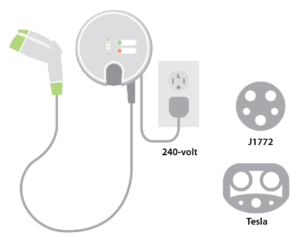
A third option is public Level 3 DC (Direct Current) fast charging. This type of unit fast charges the first 80% of the EV battery typically in 20 to 40 minutes, then tapers off reducing the charge speed during the final 20% to protect the batteries from excessive heat. There are three distinct connectors used with level three DC chargers, differentiated primarily 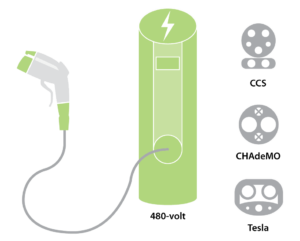
XFC (Extreme Fast Chargers) is the newest EV charging technology currently being developed in the United States. This type of car charger is capable of power outputs of up to 350 kW and higher. The U.S. Department of Energy’s Vehicle Technologies Office is working to employ this technology at scale. A challenge with this type of charging are most electric vehicles today are only capable of accepting a maximum charge rate of 50kW with some notable exceptions such as Tesla reaching 125kW. This limit is determined by the EV battery voltage and maximum amperes the wire and components can safely accept. As Level 3 and XFC charging become more ubiquitous, manufacturers will undoubtedly engineer electric vehicles to accept faster and higher kW charges further reducing charge times.
For in-home charging, the best all-around EV charging station is a level 2 unit. The level two charger is a financially feasible option maximizing charging speed with minimal electrical upgrades to a home.
Incentives for a Fast Level Two Charger at Home
The Taxpayer Certainty and Disaster Tax Relief Act of 2020 extended property tax credit for alternative refueling systems installed before 31 December 2021. For the purposes of this federal tax incentive, the IRS considers electricity as an alternative fuel. Therefore, electric vehicle chargers, if installed in a home, qualify for a 30% credit not to exceed $1,000. See IRS form 8911 rev. February 2021.
Home Performance Group EV Charger Installation in Kansas City
Interested in a level 2 AC electric vehicle charger, consider hiring an electrical professional with expert knowledge to properly design, size and install your charger and power circuit. A small upfront investment in careful design can save thousands in future repairs and mitigate the chance of a home fire.
At Home Performance Group, we continue to invest in technical training so we can correctly design, specify, size, and install electrical branch and feeder circuits. We have performed numerous EV charging station installations for our clients. If you are interested in a no cost in-home consultation, schedule with a Solutions Advisor today.
If you are interested in a no-cost in-home consultation, schedule with a Solutions Advisor today.

Article by Larry L. Motley Jr., 2 August 2021
Larry is a graduate of both Wentworth Military Academy and Missouri Western State University earning a double bachelor’s degree in Economics and Finance. Additionally, he maintains six professional tradesman licenses in two states and advanced credentialing in green technology, project and program management, and process improvement. Larry is a three-time combat veteran having served in Operation Iraqi Freedom, Operation New Dawn, and Operation Inherent Resolve. He continues to serve through a value-based building science company focused on providing clients the best design, highest quality installation, and most honest repair services in the community.


Featured Service Areas:
| Missouri | Kansas | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Belton Blue Springs Cameron Excelsior Springs Gladstone Holt |
Independence Kansas City Kearney Lathrop Lawson Lee's Summit |
Liberty North Kansas City Parkville Platte City Plattsburg Polo |
Raytown Riverside Smithville Sugar Creek Weston |
Kansas City Lansing Leavenworth Leawood Lenexa |
Merriam Mission Mission Hills Praire Village Shawnee |